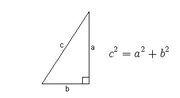
The Pythagorean Theorem states that for a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. Thus, for a right triangle where c equals the length of the hypotenuse and a and b represents the lengths of the other two sides, the Pythagorean Theorem may be depicted and represented as follows:
Using the Pythagorean Theorem, if the lengths of any two of the sides of a right triangle are known and it is known which side is the hypotenuse, the length of the remaining side may be determined from the formula.